Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) in Children and Teens Together
thinning or loss of muscles reduced ability to talk needing assistance in almost everything Food intake and metabolism Food intake and metabolism symptoms may include: weight loss little to no.
Slide Show Understanding AML
Mayo Clinic Diagnosis Bone marrow exam Enlarge image Lumbar puncture (spinal tap) Enlarge image If you have signs or symptoms of acute myelogenous leukemia, your doctor may recommend that you undergo diagnostic tests, including: Blood tests.

Acute Myeloid Leukemia What Your Patients Need to Know Hematology
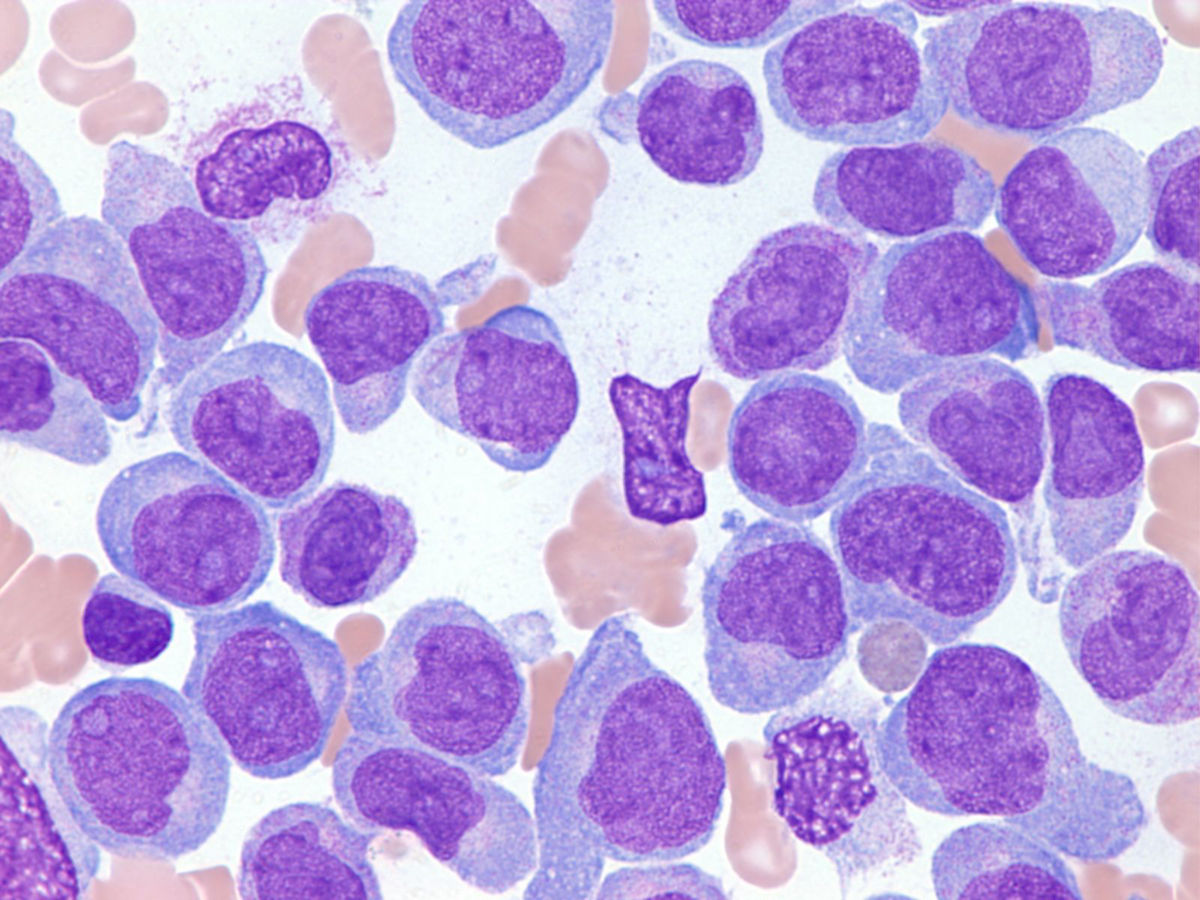
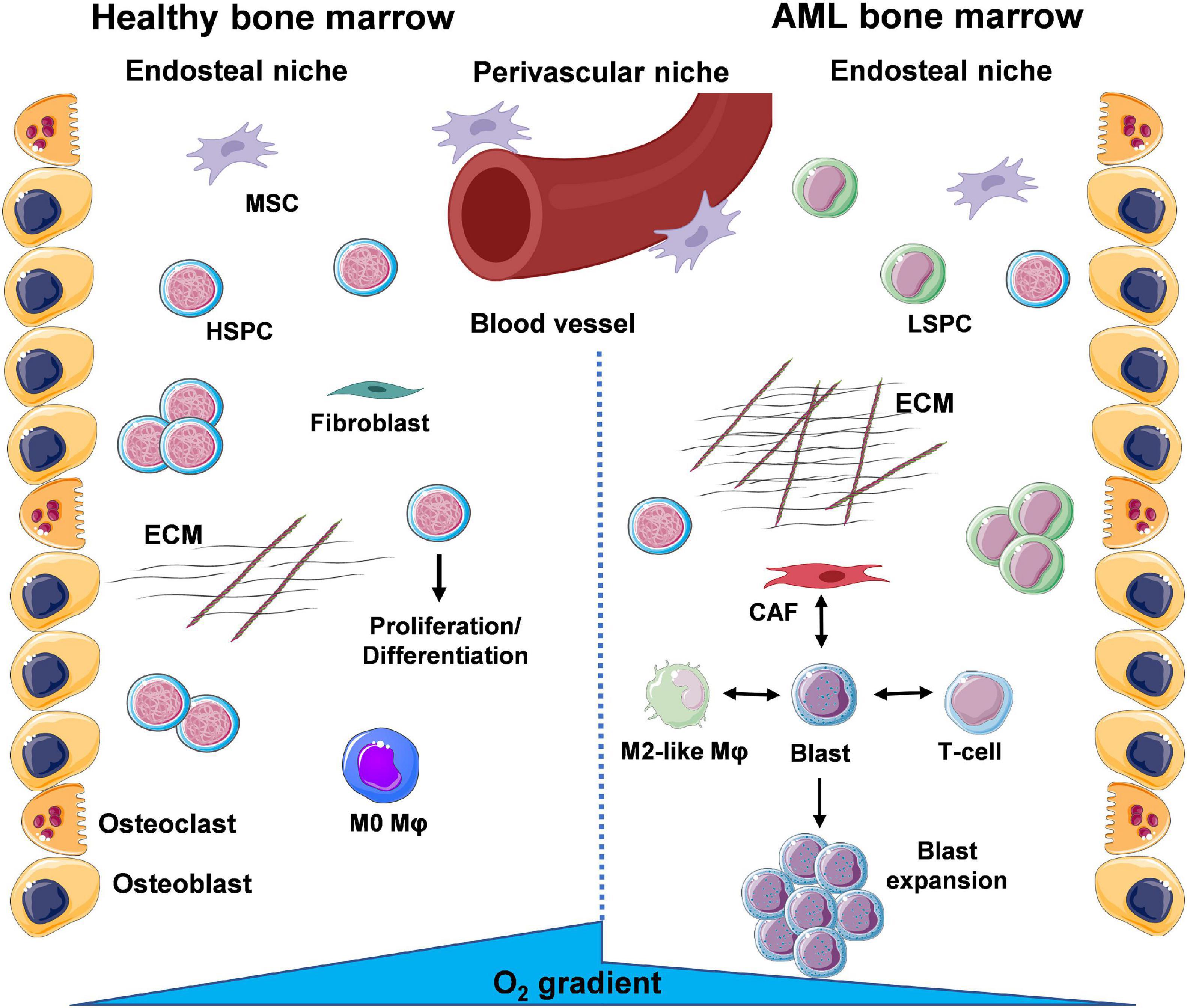
INTRODUCTION. Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) comprises a heterogeneous group of aggressive blood cell cancers that arise from clonal expansion of malignant hematopoietic precursor cells in the bone marrow. The leukemic cells interfere with production of normal blood cells, causing weakness, infection, bleeding, and other symptoms and complications.

AML patients' information Download Table
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a heterogeneous disease linked to a broad spectrum of molecular alterations, and as such, long-term disease control requires multiple therapeutic approaches. Driven.

Treatment Algorithm for Newly diagnosed patients with AML unfit for
Acute myeloid leukemia following organ transplantation (PT-AML) is a rare event with only a few published cases in the literature. We present three patients who developed AML (FAB M1, M5, M4.

(PDF) Posttransplant acute myeloid leukemia (PTAML)
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is the most common leukemia among the adult population and accounts for about 80% of all cases. It is characterized by clonal expansion of immature "blast cells" in the peripheral blood and bone marrow resulting in ineffective erythropoiesis and bone marrow failure.

2022 ELN for the diagnosis of AML in adults
INTRODUCTION Management of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is informed by the individual's medical fitness for intensive antileukemic therapy. Importantly, medical fitness is based on performance status and physiologic function, but not on age per se; we do not apply age limits when judging medical fitness. This topic discusses treatment of AML in.

LY3214996 potently inhibits proliferation of human primary patient AML
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is the most common leukemia among the adult population and accounts for about 80% of all cases. It is characterized by clonal expansion of immature "blast cells" in the peripheral blood and bone marrow resulting in ineffective erythropoiesis and bone marrow failure.

What Are My Options for AML Treatment? Patient Power
Progress in understanding the pathophysiology and improving the therapy of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is now occurring at a rapid pace.
Acute Myeloid Leukemia Could Have a New Treatment
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a heterogenous disease with a broad spectrum of cytogenetic and molecular aberrations contributing to the definition of distinct AML subgroups. Treatment options for patients suffering from AML are continuously expanding and targeted therapies are available for distinct molecularly defined subgroups.
Adult myeloid leukaemias current and future treatments The
Acute myeloid leukemia (also called AML) is a cancer of the blood and bone marrow cells. It affects a group of white blood cells called myeloid cells because they are formed in the bone marrow. "Acute" means that it develops and advances quickly, and requires immediate treatment.

Schematic outline of AML treatment protocols. (a) AML patients 60 years
Acute myeloid leukemia following organ transplantation (PT-AML) is a rare event with only a few published cases in the literature. We present three patients who developed AML (FAB M1, M5, M4) after renal, double lung or liver transplantation. Molecular analysis detected a t (9;11) in one patient and documented the recipient origin of AML in a.
Final Stages Of Aml Before Death Cemas
Due to the rarity of the disease, the characteristics of acute myeloid leukemia following solid organ transplantation (post-transplant AML; PT-AML) are unclear; furthermore, it is not known for certain whether PT-AML is a separate entity or not. We provide a systematic review of all previously reported cases of PT-AML in the English literature.
Frontiers Optimizing Transplant Approaches and PostTransplant
The prognosis for acute myeloid leukemia varies depending on age, subtype, and response to treatment. The best survival is in patients under age 20, with a five-year survival rate of 68%. For people 20 and older, the five-year survival rate is 26%. Older AML patients are more likely to have chromosomal abnormalities in their cancer cells that.
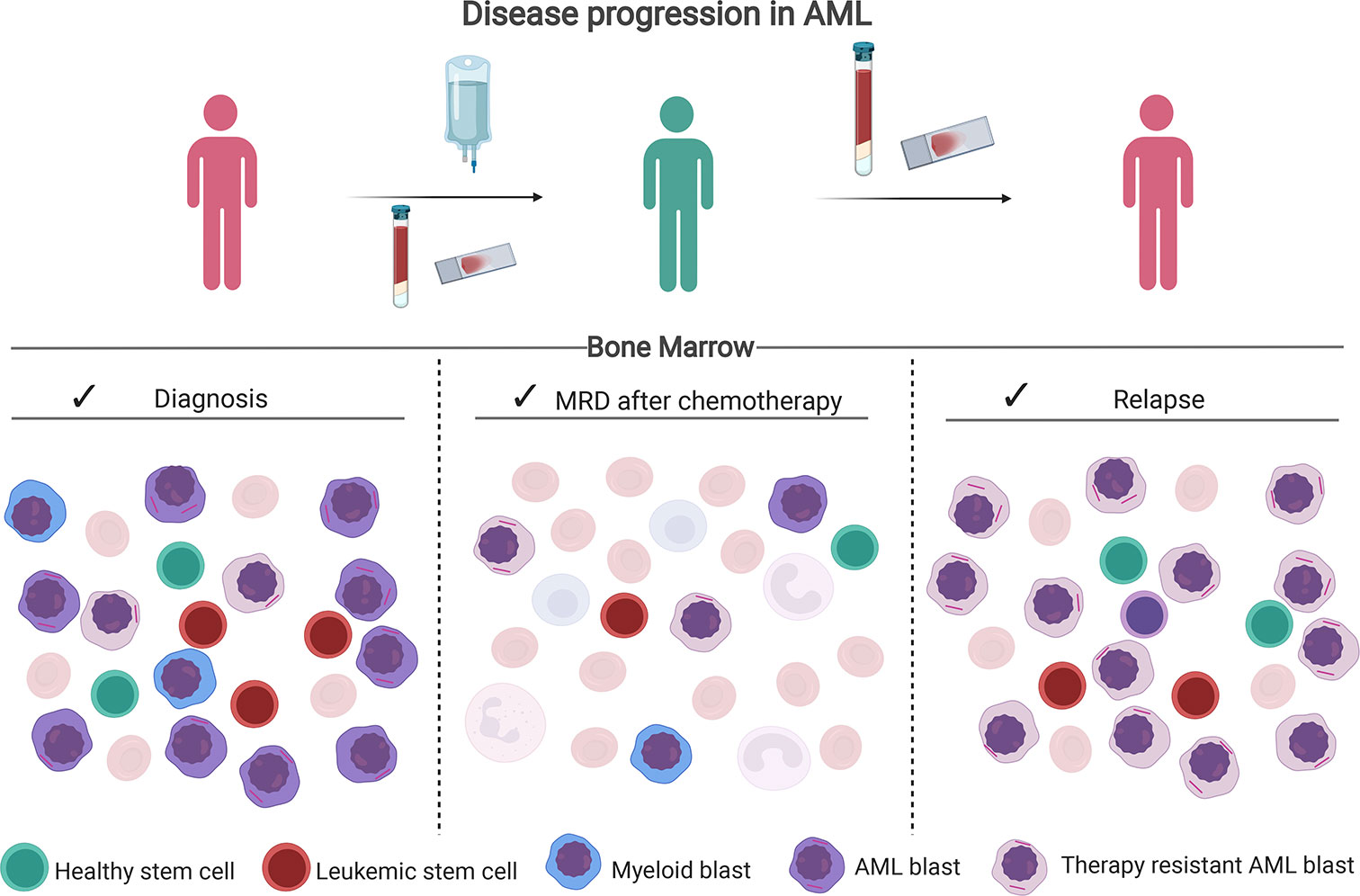
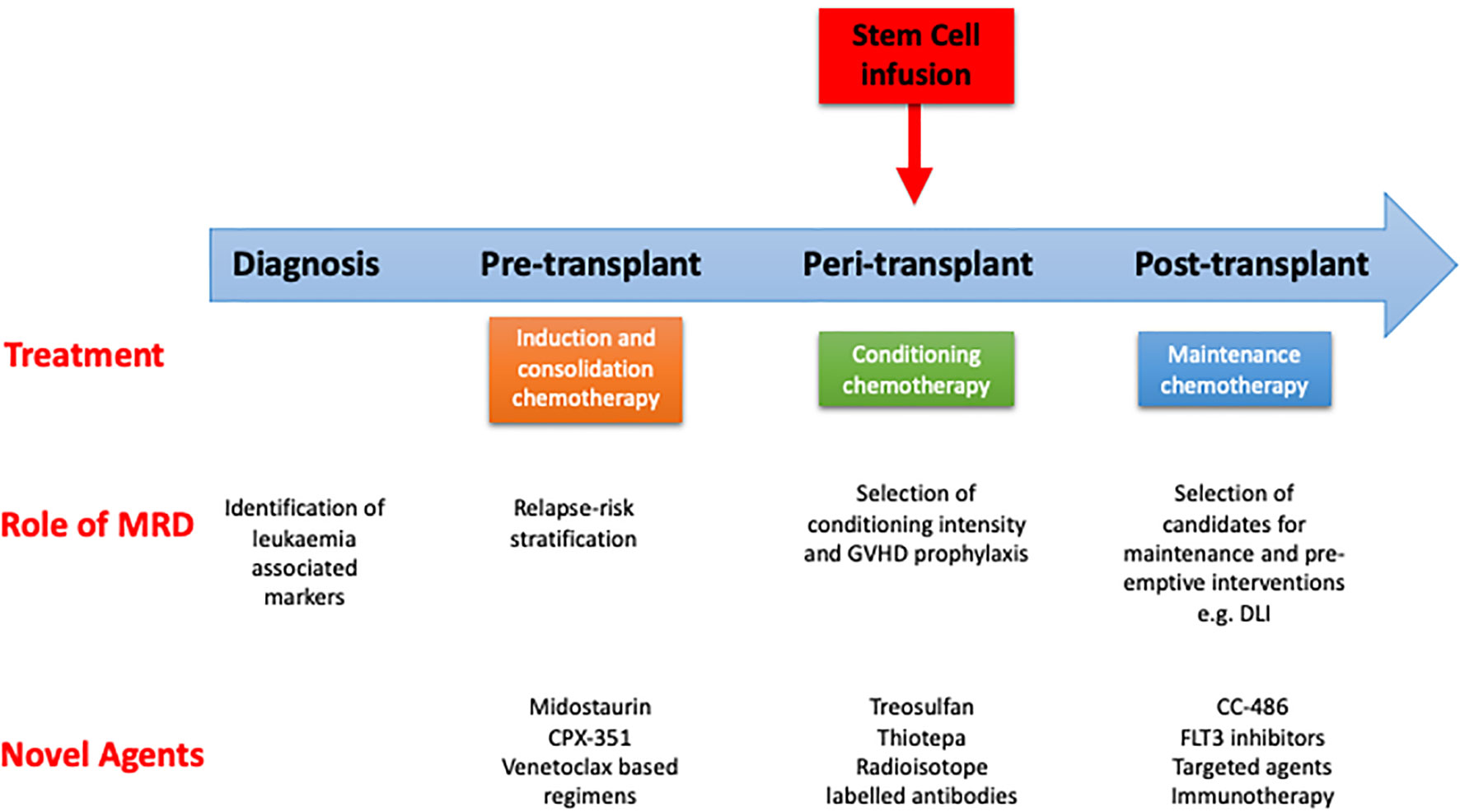
Frontiers MRD Tailored Therapy in AML What We Have Learned So Far
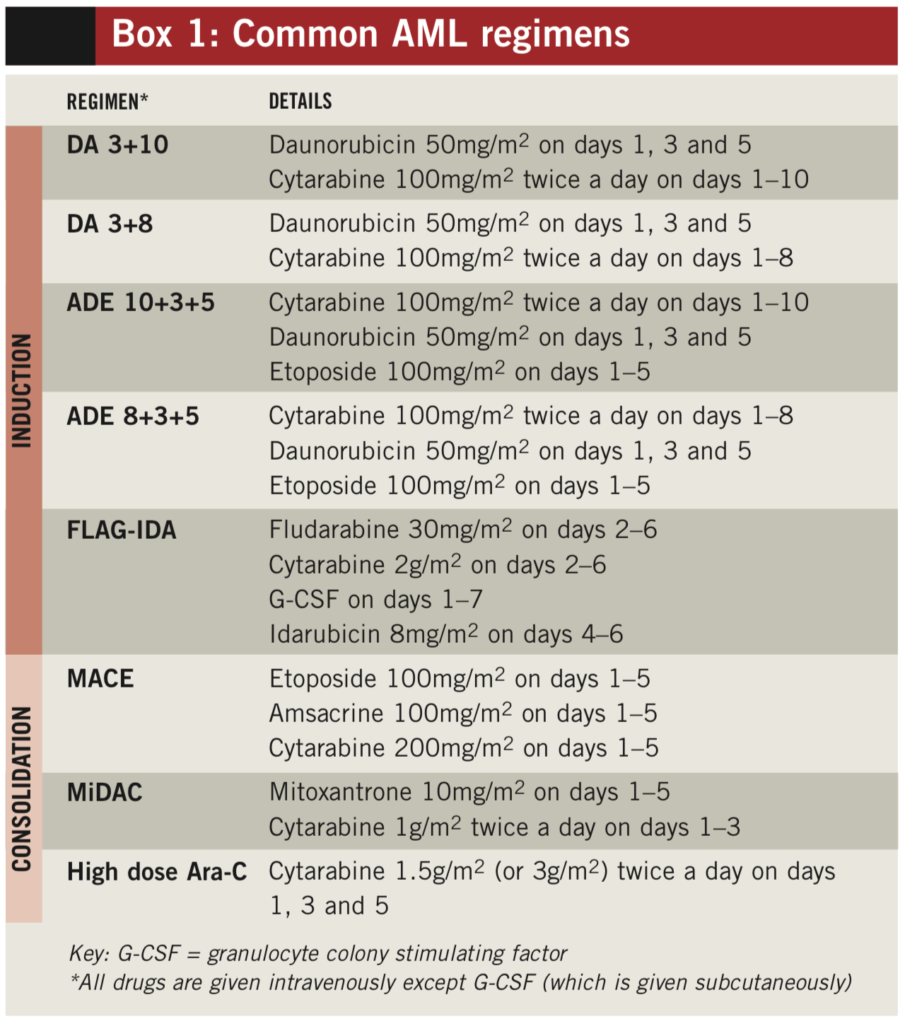
Treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is typically divided into 2 main phases: Remission induction (often just called induction); Consolidation (post-remission therapy); A third phase, known as maintenance, is sometimes used after consolidation.. Chemotherapy (chemo) is the main treatment for most types of AML, although other treatments might be used as well.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/aml-vs-cml-5198393-FINAL-cbb806d80b1a4ebf987e9efbb9636c0a.jpg)
AML (Acute) vs. CML (Chronic) Leukemia What to Know
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is the most common leukemia among the adult population and accounts for about 80% of all cases. AML is a type of cancer involving the blood and bone marrow. The main cell involved in this disorder is myeloid stem cells which can become either red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelets.